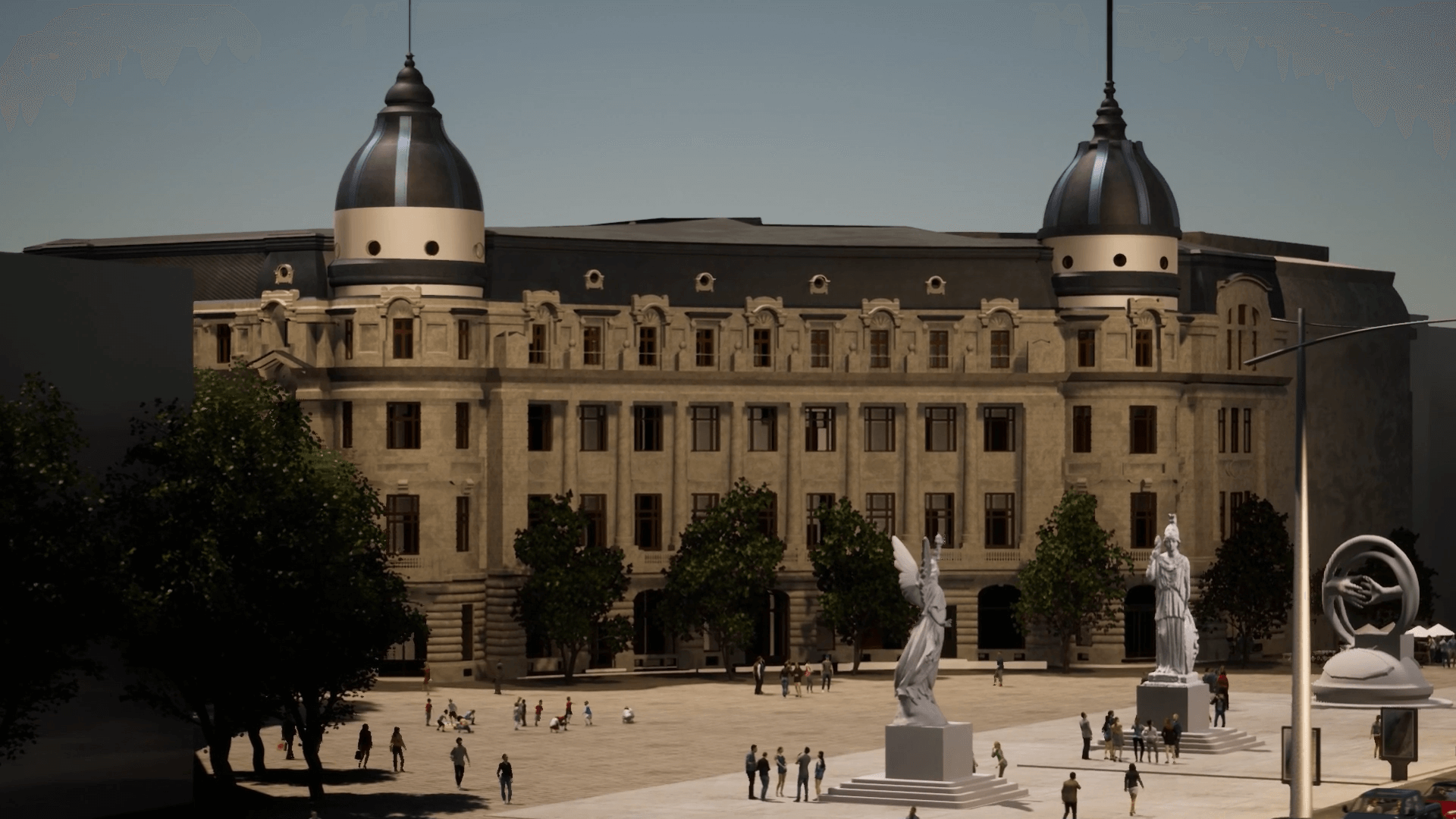
3D modeling and BIM are valuable tools for any engineer, architect or builder. The technology streamlines processes at every step, from the conceptual phase to actual construction on site. It provides accurate data that allows analysis of many parameters, including project sustainability. The results are also compatible with other leading technologies and facilitate efficient communication between team members.
A big advantage of 3D modeling is that it allows digital representation of objects that do not yet exist, making it easier for designers and architects to visualise buildings quickly and realistically. It also reproduces and displays the exact dimensions of each element, making it easier to design and complete the work.
However, 3D modeling is only a digital version of the object under construction and cannot be extended to establish intelligent building operation. This is where BIM becomes useful, storing detailed information on how the building or construction can best be exploited, but also to observe existing facilities both technologically and economically.
3D modeling is useful to represent the final appearance of a building and architectural objects, but also to evaluate the results before work starts. 3D models can also be used for digital visualisations, commercial animations and client-friendly project presentations. Furthermore, 3D modeling provides an informative model of a building and makes it easier to estimate the amount of materials needed for various maintenance works such as facade refurbishment.
BIM services can be used to train facility operators on the project and coordinate construction operations more efficiently. They are also useful for managing the life cycle of a building, from concept to completion.
3D modeling is based on using a collection of points in three-dimensional space. These are connected by lines, triangles and curved surfaces. Based on these, using texturing and shading tools, they form a complete, photorealistic, high-density 3D model.
BIM holds detailed and accurate information about a building’s structural features including walls, doors, windows, structural and electrical systems, ventilation, cooling, heating and/or plumbing. A BIM object can also be accompanied by parameters such as strength, heat, density, permeability, porosity, emissivity, electrical resistivity or reflectivity.
All this is extremely useful information in any project to track and manage the functionality, durability and sustainability of the construction.